Amaran Gemlab uses state of the art instruments such as microscopes, Refractometers, polariscopes, spectroscopes and UV-Lamps from Eickhorst, Germany for precise data processing

Microscope
An essential and very important aid for the observation of internal features such as inclusions of gemstones. The inclusions of certain minerals or gemstones are very typical for its geographical origin which will aid us identify the origin of the gemstone. By using a microscope, heat-treatments and other clarity enhancements can be identified.
Dichroscope
An instrument for detecting pleochroism in a material. It is constructed so that two pleochroic colours, or shades of colour can be detected and compared side by side in a single view. Only coloured, transparent to translucent anisotropic materials may display pleochroism.
Specific Gravity Test
Specific Gravity (SG) is the ratio of the weight of a substance to the weight of an equal volume of water. Every gem has its own specific gravity and the SG can be used as an additional value in gemstone identification. For this, a hydrostatic balance is used.
Polariscope
An optical instrument used in testing transparent and translucent gemstones to distinguish between isotropic and anisotropic materials. This instrument can be used with rough, faceted or carved gemstones.
The refractometer
This instrument measures the refractive index (RI) of gem materials which indicates the ‘optical density’ of a substance. It is related to the angles of incidence and refraction of light. The refractive index differs from gemstone species to species. Stones which are set in an item of jewellery may be possible to be tested.
Balances
Amaran Gemlab uses several different 3-digit carat balances for accurate measurement of gemstones.
The spectroscope
This is used to test transparent gemstones. This instrument measures the spectrum of visible light from violet to red by observing pure light. Some gem materials modify this white light in a way which can aid gem identification.Advanced Analytical Equipment
The following instruments are used for in-depth analysis of gemstones
FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer)


FTIR is a mandatory tool in the modern gemological laboratory. It is routinely used for testing some of the most important gems such as diamond, emerald, corundum, alexandrite, jade, amethyst, amber and turquoise.
How this works
FTIR spectrometers are used to measure absorption in materials within the infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum. In infrared spectroscopy, IR radiation is passed through a sample. Some of the infrared radiation is absorbed by the sample and some of it is transmitted. The resulting spectrum represents the molecular absorption and transmission, creating a molecular fingerprint of the sample where no two unique molecular structures produce the same infrared spectrum. This makes infrared spectrometry very useful for several types of analysis.
FTIR is used to:
- Detect polymers, oils and resins used for impregnation, e.g. in jadeite, opal or emerald
- Distinguish certain natural and synthetic gem materials, e.g. emerald, aquamarine
- Diamond analysis treatments detection
- Opinions on heat treatment on ruby and sapphire
- Works best on faceted gems but may give results even for rough stones
- Testing can be done for loose gems from 0.05 to 50+ ct
Raman Spectroscope

This is a non-destructive tool which is fast, reliable and surprisingly easy to use. Raman Spectroscope is fully automatic for gemological testing and analysis.
How this works
The gem under study is laid table down on the sample stage. Optical system of the Raman probe is automatically in focus at the sample surface. Raman spectroscopy is used to study vibrational, rotational and other low-frequency modes in gemstones and minerals. It relies on inelastic scattering or Raman (Raman effect) scattering of monochromatic light from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, photons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Raman spectrometry is a very fast and reliable tool for the identification of minerals and gemstones. This discovers the optimal measurement parameters, acquires the spectrum and finds the best matches from comprehensive spectral libraries.
Raman spectrometry is used to:
- Rapid gem identification typically between 20 seconds to 4 minutes (loose, mounted and rough)
- Analyzing inclusions to determine geographical origin
- Analyzing diamonds that have undergone High Pressure High Temperature treatment (HPHT)
- Separate synthetic materials and detect treatments and colour enhancements of gemstones
- Non destructive tool for gemmologists
- Works best on polished surfaces but can identify rough as well
UV-VIS-NIR Spectrometer
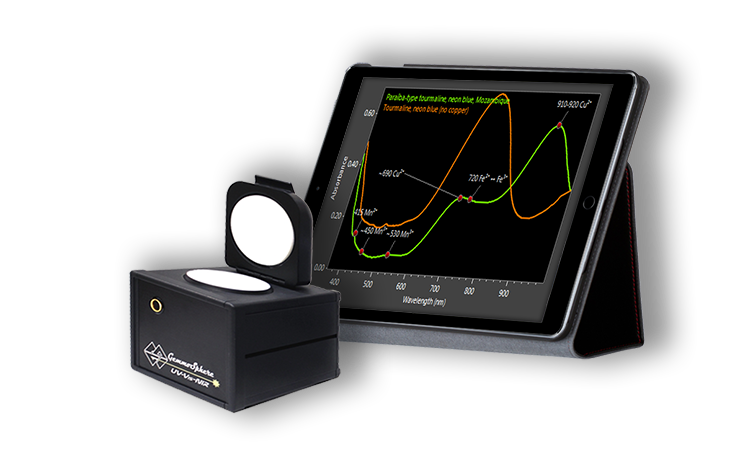
This records gemstone's absorption spectrum at near-UV, visible and near-infrared wavelengths.
The UV-VIS spectrometer is used to:
- Testing gemstones that have undergone heat treatment (such as ruby & sapphire)
- Distinguishing between synthetic and natural gemstones
- Determining the geographical origin of gems
- Enhancement identification
- Verify the natural origin of colourless diamonds as well as fancy coloured Diamonds, Sapphires, Emerald, Spinel etc
- Works for loose gemstones from 0.01 to 50+ ct
- Works best on transparents to translucent gems



